5.5 production planning
- An Minh Nguyen

- Sep 5, 2023
- 4 min read
AO2 : the supply chain process
the supply chain process: the management process of overseeing the logistics from the manufacturing stage to the finished product being delivered to the consumer
- a long and inefficient supply chain management can be costly as it increases the chances of things going wrong for the business
AO2: the differences between JIT and JIC
Just-in-time ( JIT ): a stock control system that avoids the use of holding stocks ( inventory ). Instead, stocks are supplied and delivered only when needed for production
- deliveries of stocks such as raw materials and component are a few hours prior to their use by the purchaser
- enable business to get a hold of raw materials and components only when the need arises
- allows businesses to avoid the costs of storage, maintain, theft and wastage
advantages :
foster lean production and productive efficiency
there is no need for buffer stock = cost of stock management is reduced, no need for stockpiling = improving cash flow and work capital
disadvantages :
complete reliance on third party hence inability to meet unexpected changes in demand
administrative and implementation cost of JIT are high
Just-in-case ( JIC ): a stock control system that relies on having spare stocks ( inventory ) so that output can be raised immediately in the event of a sudden or unexpected increase in demand
- cost include: insurance, maintenance, security to prevent damage or theft
- ensure the firm have sufficient amounts of inventory to meet demand
- suitable for non-perishable stocks
advantages :
enable production to continue if there is a delay in deliveries from suppliers which prevent loss of potential customers compared to if JIC system is used, hence maintained customer satisfaction as they do not have to wait for stocks to arrive
firm can benefits from purchasing economies of scale ( bulk buying )
disadvantages :
high cost : insurance, maintenance, security to prevent damage or theft, hence there could be liquidity issues because JIC ties up valuable working capital
there is also theirs of large stocks of obsolete and unsold products
AO2, AO4 : stock control charts
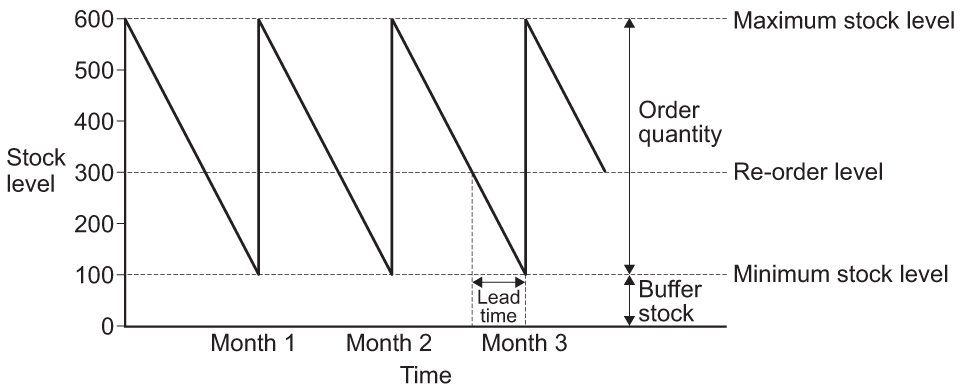
lead time : refers to the length of time it takes between a firm ordering new stock and the firm receiving the stock for production ( the longer the lead time, the earlier the re-order needs to be and the larger the re-order quantity needs to be )
buffer stock : minimum stock level held by a firm in case of late deliveries from suppliers, damaged stock or a sudden and expected increase in demand
reorder level: the stock level at the time the firm place its re-order of stock
usage rate : the speed at which stocks ( inventories ) are depleted in the production process ( 600 per month )
stock-out : occurs when a firm has no more stock for production
stockpiling : a business builds up excessive levels of inventory. ( holding too much stock results in working capital being tied up )
AO2, AO4 : capacity utilisation rate
capacity utilisation rate : expresses a firm's actual output as a percentage of its maximum potential output at a particular point in time

- a firm that has 100% capacity utilisation rate is operating at full capacity, with all its resources used
- rate can be improve by subcontracting work ( outsourcing )
advantages
average unit cost of production are likely to be at their lowest so the business is operating efficiently
lower costs per unit ( economies of scale ) will likely lead to high profits for the firm
disadvantages
employees can become overworked and stressed due to working at full capacity
machinery and equipment are likely to deteriorate at a faster pace, thus increasing maintenance and replacement costs
AO2, AO4 : productivity rate
productivity : a measure of the efficiency of production. the productivity rate measures the amount of output generated per unit of input
labour productivity :measure of the efficiency of workers in an organisation

- labour productivity can also be measured by revenue per worker or volume produced per labour hour
- labour intensive firm prefer to use this measure of productivity
capital productivity: measures how efficiently a firm's fixed asset generate output for the business
- capital intensive firms prefer to use this measure of productivity
- the higher the productivity rate, the more efficient the firm is
- high efficiency correlate with profitability and competitiveness
AO2, AO4: Cost to buy ( CBT ) and cost to make ( CTM )
a make or buy decision : a management decision which involves choosing whether to manufacture a product ( make ) or to purchase it ( buy ) form an external supplier. essentially, it is a decision about whether to insource or outsource production.
- a make or buy decision require managers to compare the cost to make and the cost to buy
CTB = Price x Quantity
CTM =Fixed cost + Variable cost
quatitative methods
breakeven analysis
investment appraisal
qualitative factors :
quality control
reliability of suppliers
the impact of workforce
experience
expertise



Comments